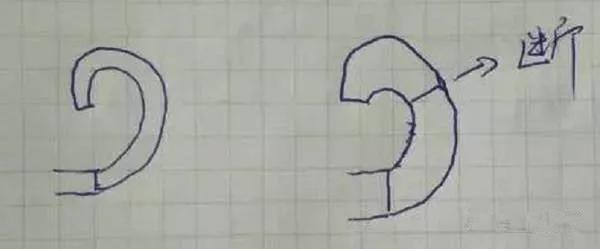Three simple solutions for turning machining
Effective chip removal avoids scratching the machined surface and prevents chips from getting stuck on the part and the tool before the second cut, so the iron chips should be broken as much as possible so that the production can be smooth and stable. So what should I do once I continue to chip?
There are three solutions:
1. Increase the depth of cut Ap
2. Increase feed F
3. Use a sharper chip breaker blade
Increasing the depth of cut and increasing the feed are all the same, that is, the strength of the iron filings is increased, so that when the same curvature is used, the iron filings can be broken.
The figure shows the situation that the iron filings are broken in the same curvature after the depth of cut. The increase of the feed is to increase the depth of cut in the axial direction, so the same reason, I will not draw.
Of course, most of the time, the depth of cut can not be adjusted, mainly to adjust the feed (preferably reduce the speed, F does not change, F increases, which can also improve the tool life). However, increasing the feed will bring corresponding problems.
Problem 1: The cutting force becomes larger, the strength requirement of the whole processing system is increased, and vibration may occur. If the vibration is not enough, other methods are needed.
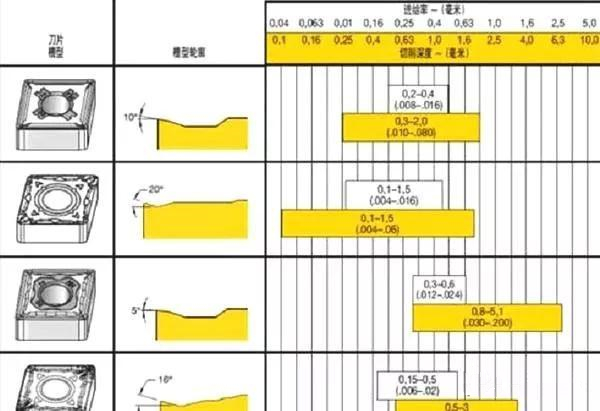
Problem 2: The finish is reduced. In the case of the same rounded corners, the increased feed finish will definitely decrease, so pay attention to the finish of the workpiece. (The relationship between fillet and feed has an empirical formula: Ra = (f * f ** 50) / re, the larger the feed, the smaller the corner of the tool tip, the greater the surface roughness value obtained) Let me talk about changing the groove type. What is a trough? In fact, each tool sample has an introduction to the chipbreaker in front of it. For example, the following one.
A chipbreaker mainly looks at the rake angle and the blade width, just like the angle marked in the “groove profile” above. The larger the angle, the larger the angle of the iron filings. The thinner the iron filings, the more likely it is. Chip breaking, so when you continue to swarf, it is necessary to look at the front angle of the blade you are using now, and then change the blade of the larger front angle for processing, the chip breaking situation will be better.
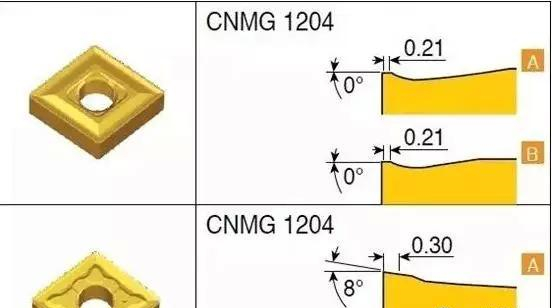
There is also a blade width, the blade width is not reflected in the above picture, but it is reflected by the depth of cut, better, that is, the depth of the blade is suitable for processing, if you use the blade continuously, then you will see Look at other blades that can cut a little lighter. Some reflect the blade width as shown below.
In the above figure, the blade width (such as 0.21) is marked. It is well understood that the smaller the blade width, the shallower it can be cut. However, the depth of cut must be about the width of the blade, otherwise it is not cutting but grinding. In short, continuous scraping, choose a smaller blade width, can cut thinner, and the chip breaking situation is better.
However, choosing a large rake angle and a small blade width will also cause problems. The blade strength is not enough, and the tool is more satisfactory. Therefore, if you choose a sharper blade and try again, you can choose a slightly softer one. It is possible to lower the point first (if efficiency is not required).
Hot tag:CNC Turning High Precision Parts,CNC Milling Precision Parts For Electronic,CNC Machined Stainless Steel Engine Parts,CNC Turning Brass Accessories,CNC Milling Anodized Parts,CNC Machining Aluminum Components